 Rules Engine
Rules Engine
With Rules Engine, you can create JSON structured business rules without the need to write code yourself.
These rules take an input, compare it against any number of conditions, and return an output based on which conditions have been met.
With this approach, you can implement a rule within scripts, processes and in the Adaptive Designer. By doing this, you can adjust the rule to change the output later and do not have to change the code.
You can call a rule inside a script the same way you call an API.
Process of creating rules
To create rules, you define attributes. These attributes define the data that are accepted by the logic of the rule. Learn how to create attributes: Create attributes for the rule
These attributes are used in a variety of conditions. Learn how to create conditions: Create a rule with conditions
Each rule can have any number of conditions. Rules follow these rules:
-
Conditions are read from top to bottom.
-
A condition consists of one or more clauses.
-
Each condition is treated as an
Ifstatement, where the incoming data is checked against the specified condition. -
If the condition is met, the
Thenresult is returned. The rule is completed. -
If the condition is not met, the next condition in the sequence is checked.
-
If no conditions are met, the rule returns
False. -
Each condition is a group, which can contain multiple clauses.
-
When there are multiple clauses in one condition, each clause within the condition is compared with an
and.
The following is an example with three condition groups.
The incoming data is passed through each group.
If the conditions are met, the Then data is output for that condition.
If all conditions are checked and no conditions are met, the rule will output False:
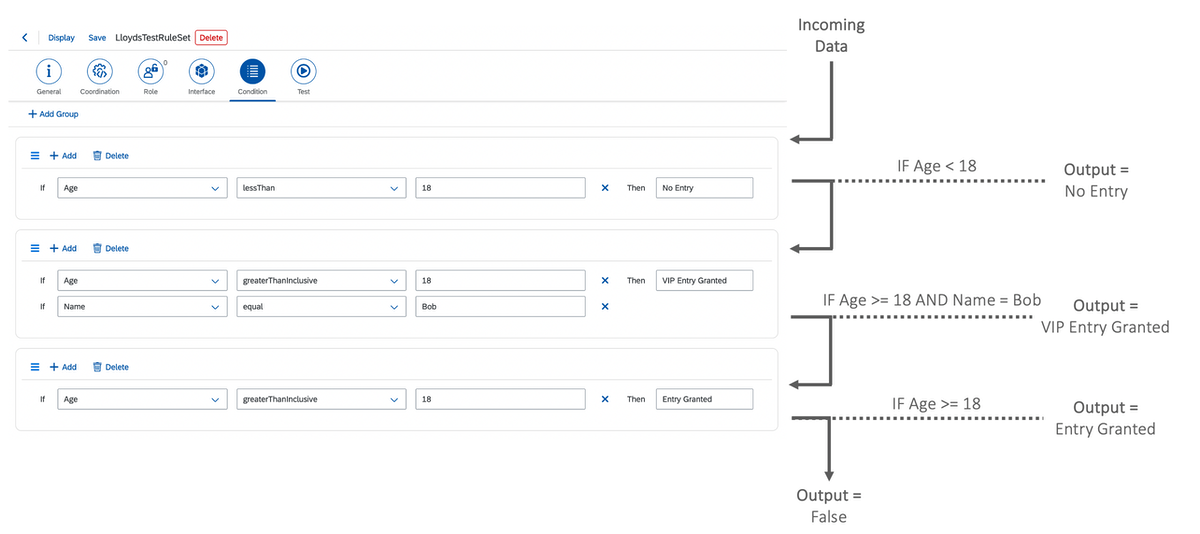
The example returns the following values in the Test tab:
| Name | Age | Result |
|---|---|---|
"" |
10 |
No Entry |
"" |
20 |
Entry Granted |
James |
25 |
Entry Granted |
Bob |
30 |
VIP Entry Granted |
Bob |
17 |
No Entry |
"" |
"" |
False |